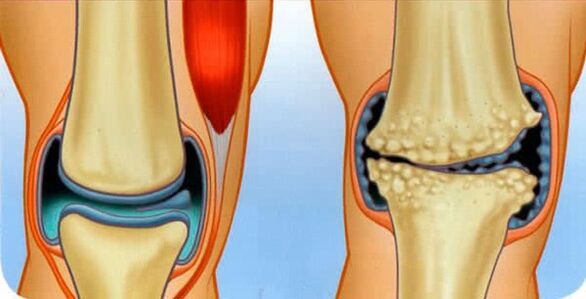
The surfaces of the bones that form the joint are covered with a special, soft, hyaline cartilage, which provides the least frictional force during the motor skills of the joint surfaces. If osteoarthritis is diagnosed, it means that the cartilage is in the process of being destroyed.
Progressing, the destructive process spreads to the bones, and then to the joint capsule.
The disease has a universal code for microbial 10 - M15-M19, classifying it as a class of pathologies of the musculoskeletal and connective tissues.
According to medical statistics, 12% of the world's population suffers from osteoarthritis, most of whom are older people, from the age of 65. However, each year there is an alarming trend towards an increase in the number of cases among young people.
The diagnosis is not fatal, but osteoarthritis is insidious with its relapses and the threat of total disability.
Origin Mechanism
The disease develops gradually, we can conditionally distinguish four stages:
- Initially, an area of cartilage that is poorly supplied with blood or damaged appears at the site of the cartilage. Gradually, in the presence of traumatic factors, the area is not restored, but, on the contrary, grows.
- The body, trying to restore the collapsed cartilage, replaces the damaged areas with mineralized tissue that does not have a clear structure. Such tissue is generally an inferior substitute for smooth, slippery, elastic hyaline cartilage.
- Gradually, the surface of the cartilage is covered with scars and bone growths - osteophytes.
- Healthy areas from the increased load several times wear out very quickly, and as a result, the entire cartilage tissue turns into one big scar.
If the pathological process is not stopped, the joint will undergo the following adverse changes:
- bones are involved in the process of destruction;
- the synovial membrane is inflamed;
- the joint capsule becomes denser, losing its elasticity;
- the lumen of the joint space decreases rapidly;
- the bones, unable to withstand friction, are deformed, like the joint as a whole;
- the tissues of the joint are reborn, so there is a complete loss of the possibility of movement.
Types of osteoarthritis
This disease affects absolutely any joint surface! At the same time, despite the same pathological mechanism, it is classified into several types.
So, depending on which joints are sick, they distinguish:
- osteoarthritis of the knee joint or patellofemoral osteoarthritis (abbreviated as gonarthrosis);
- osteoarthritis of the hip joint (abbreviated as coxarthrosis);
- arthrosis of the shoulder joint;
- interphalangeal arthrosis;
- osteoarthritis of the ankle joint;
- osteoarthritis of the hands;
- cervical osteoarthritis;
- jaw osteoarthritis;
- osteoarthritis of the metatarsophalangeal joint;
- osteoarthritis of the ilium;
- clavicular-acromial arthrosis;
- temporary osteoarthritis;
- arthrosis of the heels;
- arcuate osteoarthritis affecting the arcuate processes of the vertebrae (abbreviated as spondyloarthrosis);
- arthrosis of the facet joint of the spinal joints;
- uncovertebral osteoarthritis;
- Costovertebral osteoarthritis;
- talonavicular osteoarthritis.
According to the details of the course of the pathological process in the cartilage tissue, there are:
- deforming osteoarthritis is the name of a disease that has passed into the terminal (final) stage;
- arthrosis, - the presence of a classic inflammatory process is characteristic;
- chronic;
- acute osteoarthritis.
According to the causes of the pathology, there are:
- dystrophic arthrosis of the joints associated with a critical metabolic disorder;
- osteoarthritis of the fracture, caused by the corresponding injuries;
- post-traumatic osteoarthritis.
It is important to know! There is no arthrosis of the internal organs, for example, arthrosis of the heart is not a type of disease, but a consequence - a violation of cardiac activity due to the destruction of the cartilage of the thoracic region.
There is another classification, depending on whether the disease is independent or caused by provoking factors:
- primary - occurs in completely healthy cartilage, another name - idiopathic arthrosis or appears with age-related senile changes;
- secondary - caused by many reasons.
Osteoarthritis symptoms
There are quite typical signs of arthrosis of all localizations, which, depending on the degree of development of the pathology, differ in severity:
- pains, pain syndrome, aggravated by high humidity and hypothermia;
- decreased mobility of the joint;
- crunching, crunching and scraping sounds during movements of the articular surfaces;
- external changes in the contour of the joint;
- swelling and swelling;
- redness of the skin.
pain
The most initial signs of disorders make themselves felt by short-term mild or moderate pain, which almost never occurs at night, but usually appears only with a load on the articular surface.
When the inflammatory processes have passed into their final stage, the patient begins to feel excruciating, "biting" pain due to stagnation of blood and increased pressure in the joint bag. The pain is characterized by being of long duration, at any time of the day, and regardless of whether the affected area is at rest or in movement.
joint stiffness
This symptom is typical of a fairly advanced disease. At the same time, in the early stages, the patient still feels in the morning, after waking up, discomfort when moving in the form of a feeling of some stiffness.
With the progression of destructive reactions, the patient notes:
- limitation of the amplitude of habitual movements;
- the inability to change the position of the limbs at rest, even when trying to unfold the joint manually;
- strong fixation (contracture) in a certain position of the joint, which for a long time was in a state of lack of motor activity.
In the end, at the fourth stage of the pathology, ankylosis is formed in the form of replacement of articular tissues with scars, with a complete loss of functionality.
sounds in the joint
A crack can be accompanied by any bone and cartilage dysfunction, not just caused by osteoarthritis.
However, it is characteristic of this disease that the sound:
- occurs only in the joint that hurts;
- accompanied by difficulty in movement;
- it tends to intensify with the progression of the pathology, and enters during the formation of ankylosis.
Change the appearance of the joint.
Noticeable changes appear in the later stages. So, the axis of the affected limb is bent, and the articular region itself is disfigured - it grows in size, the shape changes ugly.
All this testifies to the irreversible destruction of the joint, inside of which new tissue has formed that does not have a specific structure.
If such a disease-causing process occurs in the knee, then the load on the ankle and metatarsophalangeal joints will increase, damaging them over time.
If the outwardly deformed part of the body is also swollen or swollen, this means inflammation of the synovial membrane, due to which synovial fluid accumulates in large quantities in the joint bag, which leads to severe pain.
Causes of osteoarthritis
Pathology can occur both in a single joint and spread to several. This disease occurs less often at a young age - there is still enough vitality for self-healing of the body.
However, for all age groups, the causes of occurrence in their direction of exposure are:
- internal: some diseases, bad habits, unbalanced diet, etc. ;
- external, - injuries, professional factor.
Internal causes are factors that cause a negative change in the joint in the form of inflammation of the joint. There are inflammations of various origins:
- infectious (E. coli and Koch's bacillus, viruses, chlamydia, staphylococci, Treponema pallidum, etc. );
- rheumatism;
- purulent arthritis;
- autoimmune nature;
- drop;
- psoriasis.
Additionally, causes of internal exposure include congenital or acquired disorders of cartilage structure and malnutrition, which may be associated with:
- genetic faults and mutations;
- intrauterine developmental abnormalities, including perinatal trauma;
- advanced age;
- osteoporosis, that is, "washing out" of the constituent elements of bone tissue;
- hormonal disorders and overload, including menopause;
- violations of normal metabolism;
- nutritional deficiencies of vitamins and minerals;
- diseases that cause muscle weakness;
- prolonged internal intoxication.
The exacerbation of many diseases of the musculoskeletal skeleton also leads to cartilage degeneration.
External causes of the development of the disease are factors that damage the joint, such as:
- frequent hypothermia;
- dislocations;
- heavy blows;
- fractures;
- meniscus injury;
- vigorous physical activity (weight lifting, for example);
- professional sports;
- joint surgery
Osteoarthritis grades
According to the clinical manifestations and the process of disease progression, four stages of arthrosis are distinguished:
- arthrosis of the 1st degree, this is the initial stage of arthrosis, which is characterized by hidden symptoms in the form of negative changes in the composition of the synovial fluid and weakening of muscle fibers, if pain appears, it is only during physical exertion;
- arthrosis of the second degree - this is already a sensation of pain due to the collapse of the joint of the bones and the formation of osteophytes, the reflex neurotrophic regulation is disturbed, and an audible crunch appears;
- arthrosis of the third degree is characterized by significant degenerative changes in the joint, its visible deformation with a curvature of the axis of the limb, the ligaments shorten, and the joint becomes pathologically mobile;
- Grade 4 osteoarthritis is complete ankylosis, complete contracture, and severe pain even at rest.
All four stages develop unevenly: during the pathological period, acute exacerbations and moments of remission are possible.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
It has been clinically proven that treatment and prevention in the form of elimination of factors provoking hyaline cartilage damage, although they do not relieve the disease at the initial stage, stop its development and restore the functionality of the joint.
Basically, the disease of small and moderate severity is treated with conservative methods. In case of severe destruction of the cartilaginous surface, which led to the destruction of the bones, surgical arthroplasty is indicated.
In this case, the fundamental principles in the treatment are:
- an integrated approach involving the use of various therapeutic methods;
- purpose, that is, the concentration of efforts on the elimination of factors and consequences that cause diseases.
Treatment with folk remedies.
Being treated comprehensively, but at home, you can additionally resort to the healing recipes of traditional healers, who offer an effective treatment of health problems through herbs and bee products.
Of the plants I use:
- bay leaf in the form of specially prepared decoctions, vodka tinctures and oils, used externally, directly on the area of inflammation;
- treatment of osteoarthritis with honey has established itself as a reliable local medicine that relieves inflammation in the form of rubbing and nourishes the skin, muscles and cartilage;
- cabbage leaf, better than white cabbage, knead a little and wrap it around a sore spot, warm it with a woolen cloth on top and keep it all night;
- aloe juice in the form of compresses and rubbing the skin;
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint with burdock also helps: the sheet is bandaged on the sore spot, which is isolated overnight.
It is important to know! Using phytotherapy, it is necessary, to enhance the effect, forget bad habits and take care of a correct diet.
Medications for osteoarthritis
Pharmacological treatment related to the classical method of therapy is divided, depending on the dosage form used, into drugs:
- external use, in the form of ointment for arthrosis, rubbing, lotions;
- injections;
- pills for osteoarthritis;
- capsules
ointments
The pharmaceutical industry produces medical ointments based on highly active natural ingredients:
- heparin ointment.
A remedy containing 1% diclofenac helps well - the gel is applied to the skin.
injections
Injections have proven themselves in treatment, not only intravenously and intramuscularly, but also directly into the affected area, for example, with non-steroidal drugs.
So, intra-articular injections are injected into the damaged joint tissues:
- glucocorticoids, which improve the nutrition of cartilage tissue, relieve inflammation and increase elasticity;
- chondroprotectors and analogues of intra-articular fluid;
- hyaluronic acid as a lubricant and analgesic.
Preparations in the form of tablets and capsules.
A special group in drug therapy are the so-called arthrosis chondroprotectors, which contain the structural elements of hyaline cartilage and thereby restore it.
These medications are available in the form of tablets and capsules intended to be taken orally through the gastrointestinal tract (orally).
In addition, patients are prescribed NSAIDs - anti-inflammatory drugs for arthrosis of the non-steroidal group, which stop acute pain and relieve exacerbations.
Analgesics are also used in the form of novocaine blockade.
Also, complex vitamins are prescribed for arthrosis.
Of the natural preparations of local action, medical bile, applied in the form of compresses to the skin, is recommended.
Exercises for osteoarthritis
Special exercises and healing gymnastics (LFK) have proven to be excellent, the complex of which provides physical activity to the diseased part of the body in a gentle and dosed way.
Dr. Bubnovsky and Evdokimenko developed their own sets of therapeutic exercises.
It is important to know! Physical exercises very effectively help restore health, but only if you resort to them at the very beginning of the development of the disease!
Massage for osteoarthritis
A very beneficial effect in medical treatment and massage, which improves microcirculation and nutrition of deep tissues.
arthritis diet
In this condition, it is important to adhere to proper and rational nutrition in order to slightly improve the patient's condition. Recommended abstinence from overeating, exclusion of animal fats and fried foods.
It is important to know! Also, in the fight for cartilage health, it is necessary to use physiotherapy in the form of magnetotherapy, electrophoresis, paraffin and therapeutic mud wraps.
What doctor treats arthritis?
First of all, with complaints of pain in the joints of the bones, you need to go to the therapist. It is he who, having summarized the patient's history and asked in detail, will refer him to the necessary narrow specialist.
They can be, depending on the cause of the disease and its type, doctors with profiles such as:
- orthopedist;
- traumatologist;
- surgeon;
- rheumatologist


















